

















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Nucleation In Condensed Matter - Unveiling the Intricacies of Phase Transitions

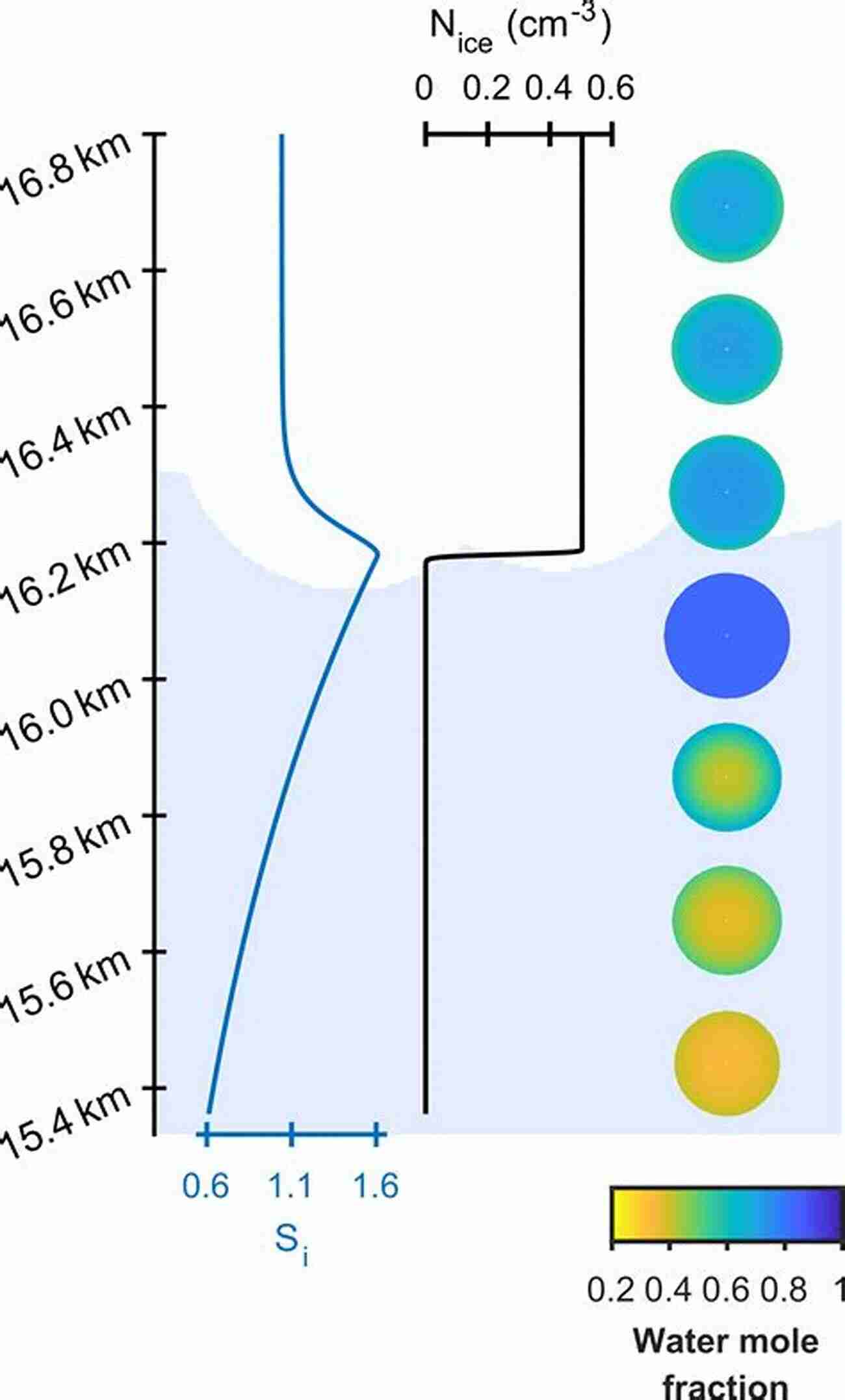
Nucleation is a fascinating phenomenon that occurs in condensed matter systems during phase transitions. It involves the formation of small clusters, or nuclei, of the new phase within the existing phase. These nuclei eventually determine the outcome of the phase transition, making the study of nucleation crucial in various fields such as physics, chemistry, materials science, and biophysics.
Understanding Phase Transitions
Before delving deeper into nucleation, it is important to comprehend the concept of phase transitions. A phase transition refers to the transformation of a system from one state of matter to another, accompanied by distinct changes in physical properties such as density, thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity.
Phase transitions can occur in numerous systems, be it the freezing of water to ice, the melting of a metal, or even the folding of proteins. These transitions are characterized by an abrupt change in the system's energy landscape, resulting from a rearrangement of its constituent particles.
4.9 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 55031 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 756 pages |
The Beginnings of Nucleation
During a phase transition, at a certain temperature and pressure, the system reaches a critical point where the new phase is favored energetically. However, transitioning to the new phase is not an instantaneous process. Instead, nucleation takes place, marking the initiation of the new phase within the existing phase. The phenomenon of nucleation can be understood through two key components: energy barriers and fluctuations.
Energy Barriers
For nucleation to occur, energy barriers need to be overcome. These barriers arise due to the free energy difference between the existing phase and the new phase. The free energy tends to favor the existing phase, making it unfavorable for the system to spontaneously convert to the new phase.
Overcoming these energy barriers requires an input of external energy or the assistance of other factors such as temperature changes, pressure fluctuations, or the of foreign particles. Once the energy barriers are surpassed, the nucleation process can commence.
Fluctuations
Fluctuations play a crucial role in the formation of nucleation. These fluctuations occur naturally in any system and can cause temporary deviations from the average state of the system. In the context of nucleation, fluctuations can lead to the spontaneous formation of small clusters of the new phase, which act as the embryos for further growth.
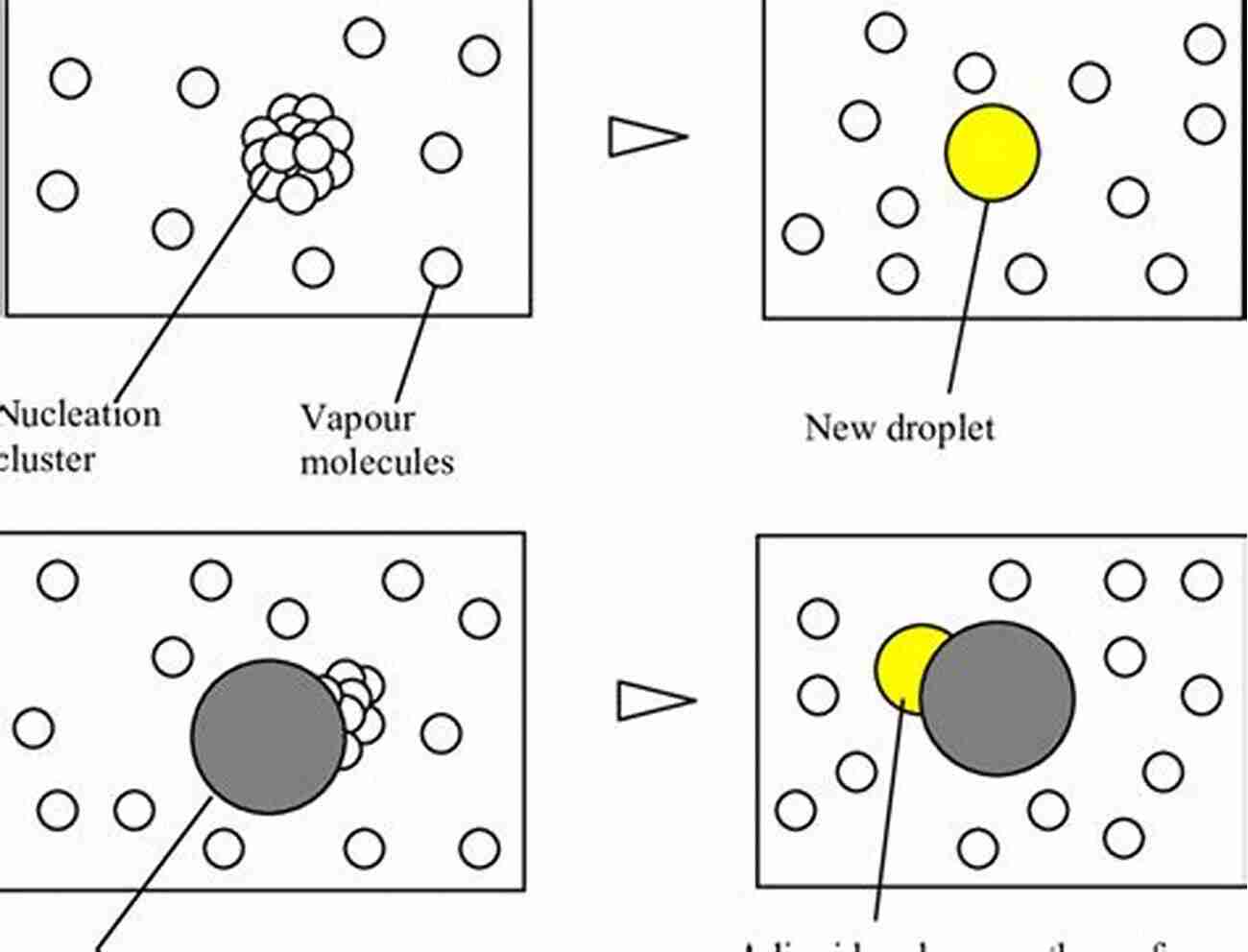
Nucleation Process
The nucleation process involves the formation and growth of small clusters that act as precursors to the new phase. These clusters, or nuclei, can form with the help of fluctuations, as mentioned earlier. Once a critical nucleus forms, its subsequent growth occurs through the incorporation of surrounding particles.
As the nuclei grow, they start competing for available particles in the existing phase. When enough particles are incorporated into a nucleus, it reaches a critical size, known as the critical radius. Beyond this radius, the nucleus can grow on its own without the assistance of fluctuations and becomes more stable.
Applications of Nucleation
The study of nucleation is crucial in various fields and has practical applications that impact our daily lives. Some notable areas where nucleation plays a significant role include:
- Metallurgy: Nucleation is vital in understanding processes like casting, solidification, and grain formation in metals, enabling the production of materials with desired properties.
- Pharmaceuticals: Nucleation impacts drug formulation, as it affects the production and crystallization of pharmaceutical compounds.
- Climate Science: Understanding nucleation allows scientists to study cloud formation, which plays a vital role in climate patterns and weather predictions.
- Biophysics: Nucleation is relevant in understanding protein folding, a process central to many diseases and drug design.
Nucleation in condensed matter systems unlocks the mysteries of phase transitions and provides insights into a wide range of scientific disciplines. By comprehending the intricacies of nucleation, scientists can manipulate and control phase transitions, leading to advancements in materials science, medicine, and climate research.
4.9 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 55031 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 756 pages |
In Nucleation in Condensed Matter, key theoretical models for nucleation are developed and experimental data are used to discuss their range of validity. A central aim of this book is to enable the reader, when faced with a phenomenon in which nucleation appears to play a role, to determine whether nucleation is indeed important and to develop a quantitative and predictive description of the nucleation behavior. The third section of the book examines nucleation processes in practical situations, ranging from solid state precipitation to nucleation in biological systems to nucleation in food and drink. Nucleation in Condensed Matter is a key reference for an advanced materials course in phase transformations. It is also an essential reference for researchers in the field.
- Unified treatment of key theories, experimental evaluations and case studies
- Complete derivation of key models
- Detailed discussion of experimental measurements
- Examples of nucleation in diverse systems

 Allen Ginsberg
Allen GinsbergKathy Santo Dog Sense Kathy Santo - Unlocking the secrets...
Are you a dog lover who...

 Raymond Parker
Raymond Parker10 Presidents Who Were Killed In Office - Shocking Truth...
Throughout history, the role of a president...

 Isaac Asimov
Isaac AsimovUnveiling a World of Magic: Beautifully Illustrated...
Bedtime stories have always held a...

 James Joyce
James JoyceThe Blind Parables: An Anthology Of Poems
For centuries, poetry has...

 Clay Powell
Clay PowellRival Conceptions Of Freedom In Modern Iran
The Struggle for Freedom in...

 Cristian Cox
Cristian CoxAdvances In Their Chemistry And Biological Aspects
In recent years,...

 Dominic Simmons
Dominic SimmonsGetting Into Mini Reefs For The Marine Aquarium
Are you interested in enhancing the...

 Vincent Mitchell
Vincent MitchellExploring the Intriguing Connection Between History,...
When one thinks of Chinese martial...

 Christian Barnes
Christian BarnesMighty Meg And The Accidental Nemesis: Unleashing the...
In the world of superheroes, there are many...

 Kirk Hayes
Kirk HayesA Journey through the World of Nhb Drama Classics: Full...
Welcome to a fascinating exploration of Nhb...

 Gerald Bell
Gerald BellWeed Cross Stitch Pattern Rachel Worth - The Perfect...
Are you a stoner who loves a little...

 Ernesto Sabato
Ernesto SabatoDiscover the Breathtaking Beauty of the South West Coast...
Are you ready for an...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Hudson Hayes"Visions Of Northland: Discover the Breathtaking Beauty and Cultural Richness...
Hudson Hayes"Visions Of Northland: Discover the Breathtaking Beauty and Cultural Richness... F. Scott FitzgeraldFollow ·18.3k
F. Scott FitzgeraldFollow ·18.3k Mason PowellFollow ·19.6k
Mason PowellFollow ·19.6k Charles BukowskiFollow ·15k
Charles BukowskiFollow ·15k Richard WrightFollow ·17.6k
Richard WrightFollow ·17.6k Percy Bysshe ShelleyFollow ·9.9k
Percy Bysshe ShelleyFollow ·9.9k Hugh BellFollow ·2.9k
Hugh BellFollow ·2.9k Allen GinsbergFollow ·14.8k
Allen GinsbergFollow ·14.8k Will WardFollow ·18.1k
Will WardFollow ·18.1k




















