















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The Intriguing Behavior of Radionuclides in the Environment: Unveiling Nature's Hidden Secrets


When we talk about the environment, various elements come to mind—fresh air, lush landscapes, and vibrant ecosystems. However, an invisible, yet incredibly impactful, group of elements exists that significantly shapes our understanding of environmental dynamics: radionuclides. These fascinating particles, formed by radioactive decay, possess unique characteristics that greatly influence their behavior and presence in our surroundings.
The Nature of Radionuclides
Radionuclides are unstable atomic nuclei that emit radiation during their decay process. They can be naturally occurring or human-made through activities such as nuclear power generation or scientific research. These particles have a broad range of half-lives, which determine their rate of decay—a characteristic that profoundly affects their behavior in the environment.
The interactions between radionuclides and the environment are complex and multifaceted. Let us explore some of the most intriguing aspects of their behavior:
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 3133 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 71 pages |
1. Mobility
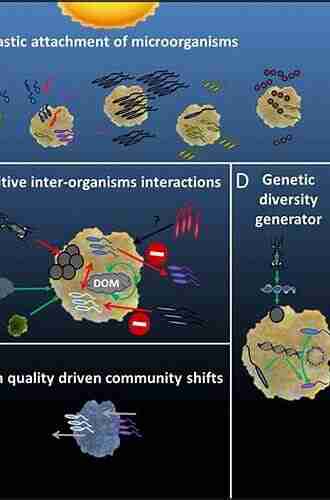
Radionuclides exhibit varying degrees of mobility depending on their properties and environmental conditions. Some radionuclides can easily dissolve in water, allowing for rapid movement through soil, sediments, and waterways. Others may bind to solid particles or organic matter, impacting their transport in the environment.
Additionally, soil properties such as pH, organic matter content, and clay content can influence radionuclide mobility. Understanding how these factors interact helps researchers predict and manage the spread of radionuclides, ensuring the safety of both human and ecological systems.
2. Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification
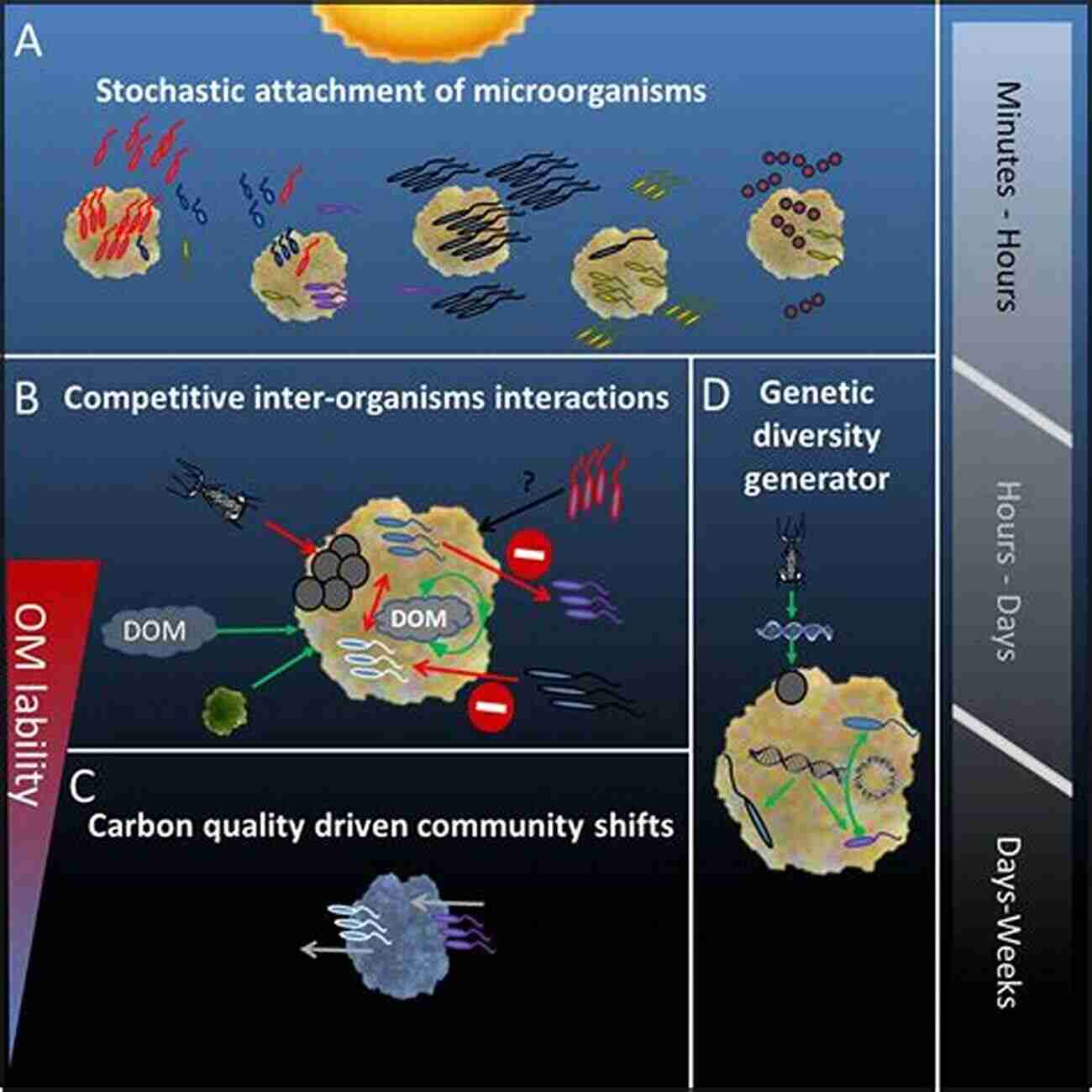
Radionuclides have the potential to accumulate in living organisms through various pathways. Bioaccumulation occurs when organisms take up radionuclides faster than their excretion rates, resulting in increased internal concentrations.
Furthermore, the phenomenon of biomagnification occurs when radionuclides are passed from one organism to another through the food chain. As predators consume smaller organisms containing radionuclides, the concentration of these elements intensifies at each trophic level.
The ramifications of bioaccumulation and biomagnification can be severe, leading to detrimental health effects on humans and wildlife. Therefore, studying the behavior of radionuclides in the environment is crucial for managing and mitigating these risks.
3. Long-Term Persistence
Some radionuclides remain in the environment for extended periods due to their long half-lives. This persistence poses long-term challenges for environmental remediation and protection.
Ongoing research aims to understand the factors that affect radionuclide persistence and develop strategies to optimize their containment or removal. These efforts contribute to safeguarding our environment for present and future generations.
4. Radioactive Decay and Transformation

The radioactive decay of radionuclides is central to their behavior in the environment. Through particle emission or decay chains, radionuclides transform into other elements, each with its own unique properties and behavior.
This decay process allows scientists to trace the movement and fate of radionuclides in environmental systems. By analyzing the radioactive decay products, researchers gain valuable insights into the behavior and movement of radionuclides over time.
5. Environmental Exposure Assessment
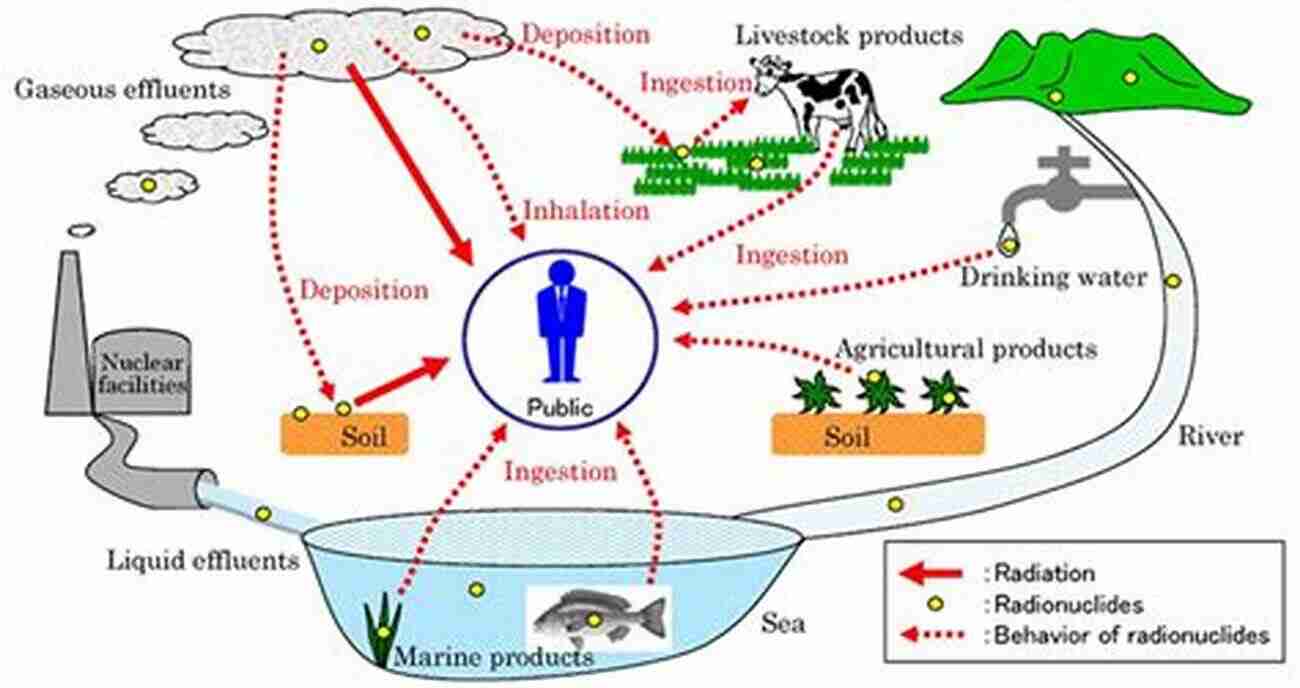
Effectively assessing the potential environmental exposure to radionuclides is crucial for risk management and protection. Researchers employ sophisticated modeling techniques to evaluate the behavior of radionuclides in various environmental compartments.
These models consider intricate factors such as radioactive decay, transport mechanisms, and biogeochemical processes to simulate the behavior and distribution of radionuclides. By better understanding their behavior, we can implement targeted measures to minimize exposure and its associated risks.
The behavior of radionuclides in the environment is a captivating area of study, offering insights into the intricate processes that shape our world. From their mobility and bioaccumulation to long-term persistence, these remarkable particles provide invaluable knowledge for environmental management, protection, and hazard reduction.
Continued research in the field of radionuclide behavior helps us navigate the complexities of our environment while ensuring the safety and well-being of both ecosystems and human populations. Embracing the challenges they pose allows us to unravel the secrets hidden within nature and forge a sustainable future.
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 3133 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 71 pages |
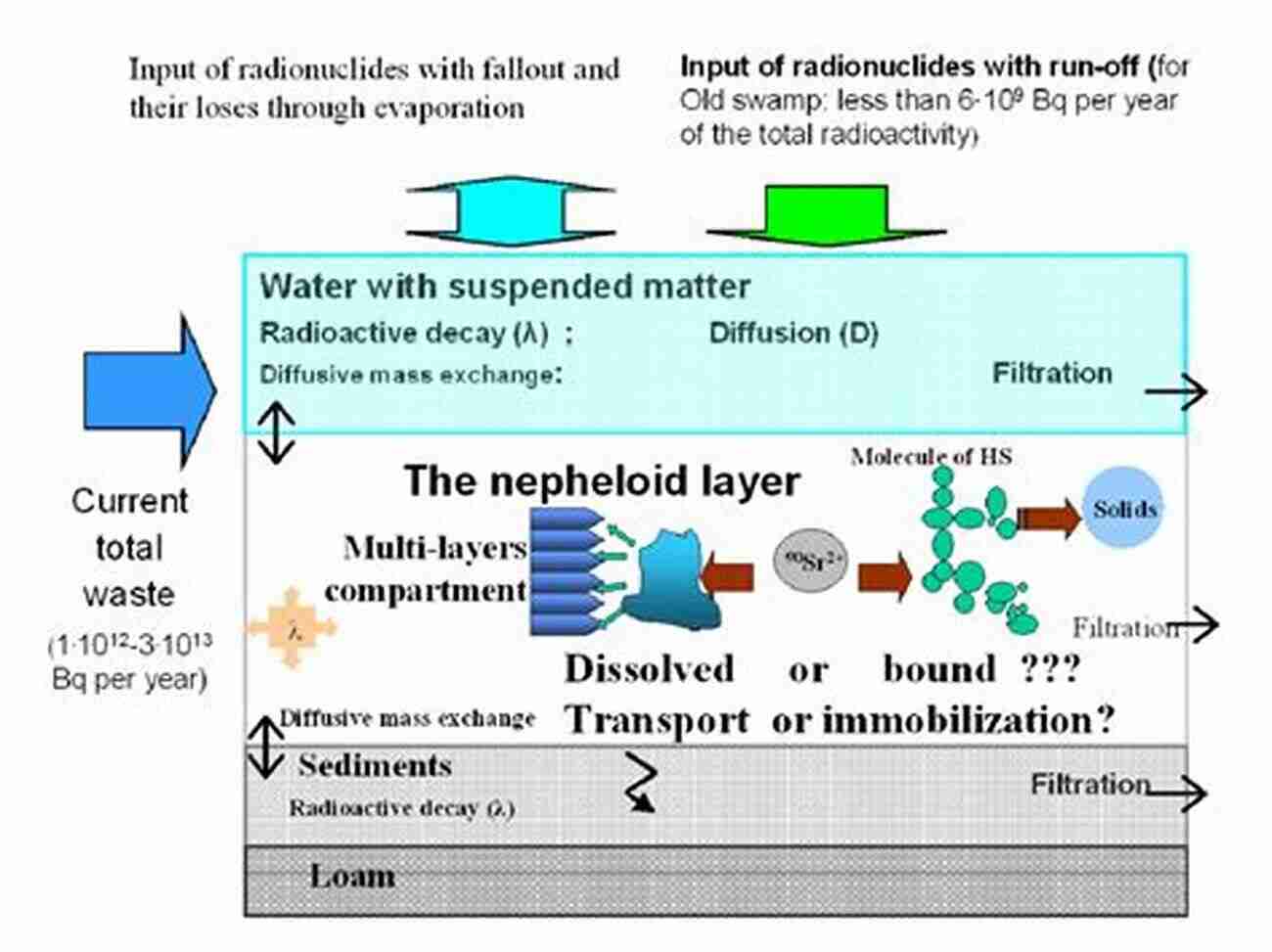
The 3-volume set highlights the behavior of radionuclides in the environment and focusing on the development of related fields of study, including microbiology and nanoscience. In this context, it discusses the behavior of radionuclides released in areas of Lake Karachai in Ural, and those released as a result of Chernobyl accident (1986),and in Fukushima (2011).
Volume I presents the experiences gained in South Urals (“Mayak” plant, Lake Karachai),providing a scientific basis for more precise understanding of the behavior of radionuclides in complex subsurface environments. On the basis of monitoring data, it examines the pathways of radionuclide migration and the influence of the geological environment and groundwater on the migration, with a particular focus on particles from the nanoscale to microscale. It also discusses the function of microbes and microscale particles, from their direct interaction with radionuclides to their ecological role in changing the physic-chemical condition of a given environment. Lastly, the protective properties of geological media are also characterized, and mathematical modeling of contaminant migration in the area of Lake Karachai is used to provide information regarding the migration of radionuclides.

 Allen Ginsberg
Allen GinsbergKathy Santo Dog Sense Kathy Santo - Unlocking the secrets...
Are you a dog lover who...

 Raymond Parker
Raymond Parker10 Presidents Who Were Killed In Office - Shocking Truth...
Throughout history, the role of a president...

 Isaac Asimov
Isaac AsimovUnveiling a World of Magic: Beautifully Illustrated...
Bedtime stories have always held a...

 James Joyce
James JoyceThe Blind Parables: An Anthology Of Poems
For centuries, poetry has...

 Clay Powell
Clay PowellRival Conceptions Of Freedom In Modern Iran
The Struggle for Freedom in...

 Cristian Cox
Cristian CoxAdvances In Their Chemistry And Biological Aspects
In recent years,...

 Dominic Simmons
Dominic SimmonsGetting Into Mini Reefs For The Marine Aquarium
Are you interested in enhancing the...

 Vincent Mitchell
Vincent MitchellExploring the Intriguing Connection Between History,...
When one thinks of Chinese martial...

 Christian Barnes
Christian BarnesMighty Meg And The Accidental Nemesis: Unleashing the...
In the world of superheroes, there are many...

 Kirk Hayes
Kirk HayesA Journey through the World of Nhb Drama Classics: Full...
Welcome to a fascinating exploration of Nhb...

 Gerald Bell
Gerald BellWeed Cross Stitch Pattern Rachel Worth - The Perfect...
Are you a stoner who loves a little...

 Ernesto Sabato
Ernesto SabatoDiscover the Breathtaking Beauty of the South West Coast...
Are you ready for an...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Alexander BlairDiscover the Unbelievable Story of How This Man's Shoes Were Far Too Tight!
Alexander BlairDiscover the Unbelievable Story of How This Man's Shoes Were Far Too Tight!
 Zadie SmithKiller Air Mud Blood And Motocross: Exploring the Adrenaline-Fueled World of...
Zadie SmithKiller Air Mud Blood And Motocross: Exploring the Adrenaline-Fueled World of...
 Javier BellThe Fascinating World of Ginzburg Landau Theory Of Condensates: Unveiling the...
Javier BellThe Fascinating World of Ginzburg Landau Theory Of Condensates: Unveiling the... Douglas FosterFollow ·6.1k
Douglas FosterFollow ·6.1k Alec HayesFollow ·8.4k
Alec HayesFollow ·8.4k Allan JamesFollow ·8.5k
Allan JamesFollow ·8.5k Earl WilliamsFollow ·9.3k
Earl WilliamsFollow ·9.3k Dillon HayesFollow ·7.7k
Dillon HayesFollow ·7.7k Devin CoxFollow ·12.7k
Devin CoxFollow ·12.7k Henry Wadsworth LongfellowFollow ·2.4k
Henry Wadsworth LongfellowFollow ·2.4k Clarence BrooksFollow ·4k
Clarence BrooksFollow ·4k